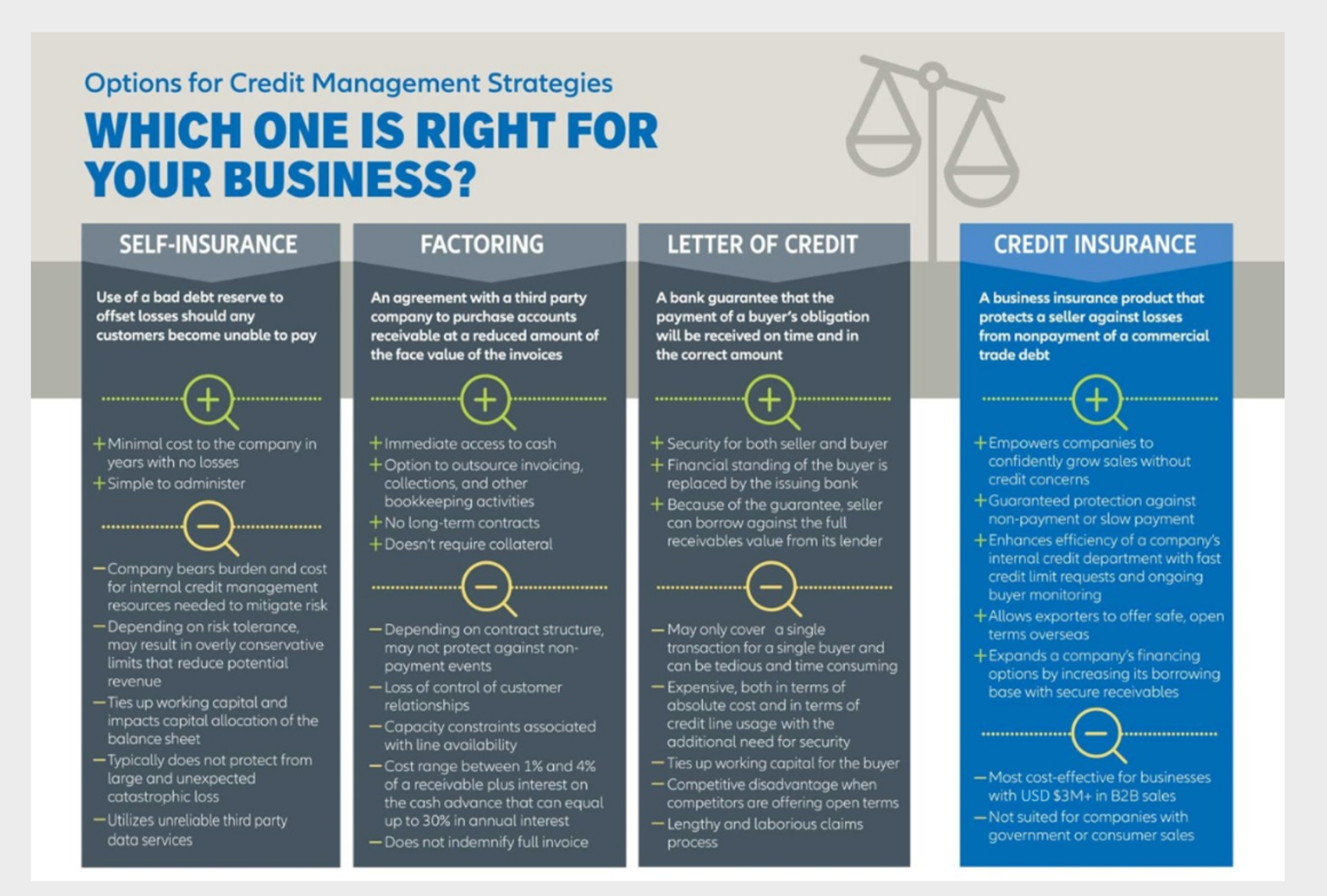
Recap: Bad Debt Reserves vs. Factoring vs. Letter of Credit vs. Credit Insurance
Option 1: Self-Insurance (Bad Debt Reserve)
Definition: Use of a bad debt reserve to offset losses should any customers become unable to pay
Pros of Bad Debt Reserves:
- Minimal cost to the company in years with no losses
- Simple to administer
Cons of Bad Debt Reserves:
- Company bears burden and cost for internal credit management resources needed to mitigate risk
- Depending on risk tolerance, may result in overly conservative limits that reduce potential revenue
- Ties up working capital that impacts capital allocation of the balance sheet
- Typically does not protect from large and unexpected catastrophic loss
- Utilize unreliable third party data services